扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘莎, 金东, 王艺婷, 王怡婷, 杨晶, 周娟, 许彦梅, 白向宁, 濮吉, 兰瑞廷, 熊衍文, 徐建国
- LIU Sha, JIN Dong, WANG Yi-ting, WANG Yi-ting, YANG Jing, ZHOU Juan, XU Yan-mei, BAI Xiang-ning, PU Ji, LAN Rui-ting, XIONG Yan-wen, XU Jian-guo
- 儿童脑膜炎大肠埃希菌毒力基因ibeC的分布研究
- Distribution of virulent gene invasin of brain endothelial cells C of neonatal meningitis Escherichia coli
- 疾病监测, 2015, 30(5): 376-380
- Disease Surveillance, 2015, 30(5): 376-380
- 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2015.05.009
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2015-01-10
2. 感染性疾病诊治协同创新中心, 浙江 杭州 310003;
3. 新南威尔士大学, 生物技术和生物分子科学学院, 澳大利亚新南威尔士州, 悉尼
2. Collaborative Innovation Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, Hangzhou 310003, China;
3. School of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, University of New South Wales, Sydney, NSW, Australia
引起儿童细菌性脑膜炎的大肠埃希菌(Escherichia coli),称为脑膜炎大肠埃希菌(neonatal meningitis Escherichia. coli,NMEC)。NMEC引起的脑膜炎,占儿童脑膜炎的80%左右[1]。NMEC可以突破血脑屏障,侵袭脑微血管内皮细胞(human brain microvascular endothelial cells,HBMEC)。已经报道的NMEC主要毒力基因有:外膜蛋白A基因(outer membrane protein A,ompAi),脑内皮细胞侵袭素相关基因(invasin of brain endothelial cells,ibeA,ibeB,ibeC),丙烯醛基硫酸脂酶样生化酶基因(acrylsulfatase-like enzyme,aslA)等[2]。有研究发现ibeC基因和侵入脑微血管内皮细胞有关[3],有可能是重要的毒力基因之一。但研究发现,所有检测到的E.coli均携带ibeC基因。提示该基因和致病性的关系有待于进一步确证。本研究通过生物信息学方法,对GenBank现存并公开释放的1620株不同来源、不同致病表型的E.coli进行了ibeC基因的检测与比较分析,为了说明这些菌株分布的代表性,对所选菌株进行了多位点序列分型(multi locus sequence typing,MLST)分析。
1 材料与方法 1.1 数据GenBank现存并公开释放的1620株E.coli基因组数据,MLST数据库72株ECOR菌株信息。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 数据下载通过文件传输协议客户端软件FileZilla下载GenBank(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/)E.coli基因组数据。下载MLST E.coli数据库中(http://mlst.warwick.ac.uk/mlst/dbs/Ecoli)ECOR菌株ST型别信息。
1.2.2 ibeC基因检测及比较分析通过序列比对程序BLAST比对检测1620株E.coli基因组中ibeC基因信息,使用序列比对软件Clustal X1.83 对E.coli代表菌株(表 1)ibeC基因序列进行多序列比对分析。
1.2.3 MLST序列分析采用E.coli MLST 数据库提供的E.coli MLST 分型方案,选择7个管家基因adk、fumC、gyrB、icd、mdh、purA、recA,对菌株进行MLST 分型分析。通过等位基因查找及比对,截取1620株E.coli基因组中7个管家基因。将截取的序列在E.coli MLST 数据库中进行比对,受试菌株序列与库中菌株序列相似性为100%时,认为等位基因序列号相同。7 个管家基因序列号的组合即为该菌的ST 型(sequence type,ST)。采用BioNumerics V 4.0软件对不同来源菌株的不同ST型别构建最小生成树,分析菌株之间的种群结构。
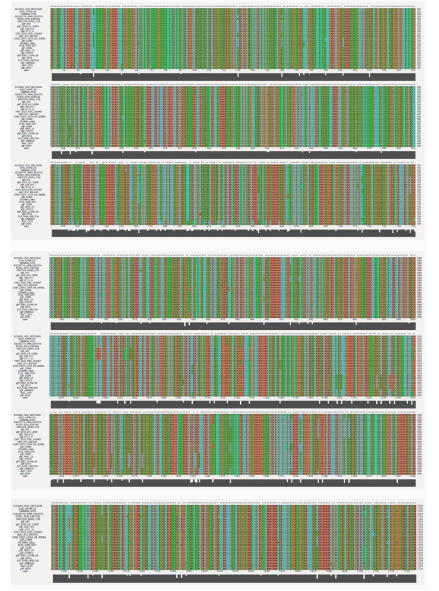
2 结果 2.1 ibeC基因检测及比较分析经ibeC特异基因检测发现1620株E.coli全部携带ibeC基因,比对选用参考序列为脑膜炎相关E.coli O7_K 1_CE 10菌株的ibeC基因,基因长度为1734 bp,经检测比对,1620株E.coli菌株ibeC序列长度均为1734 bp,与CE 10菌的ibeC基因长度一致。在核苷酸水平上,菌株携带ibeC基因与参考序列ibeC相似性高,其中序列最低相似值为96.42%,1620株菌ibeC序列平均相似值为98.21%。表 1所示菌株中ibeC基因多序列比对结果详见图 1。
| 菌株 | 菌株详细信息 | ||||
| 基因 | 分类 | 系统发生组 | 序列型 | 分离来源 | |
| MG1655 | eptC(yijP) | Commensal | A | 10 | Human |
| HS | EcHS_A4189 | Commensal | A | 46 | Human |
| ETEC_H10407 | ETEC_4223 | ETEC | A | 48 | Human |
| SE11 | ECSE_4248 | Commensal | B1 | 156 | Human |
| IAI1 | yijP | Commensal | B1 | 1128 | Human |
| 55989 | yijP | EAEC | B1 | 678 | Human |
| E24377A | EcE24377A_4494 | ETEC | B1 | 1132 | Human |
| O26:H11_11368 | yijP | EHEC | B1 | 21 | Human |
| O103:H2_12009 | yijP | EHEC | B1 | 17 | Human |
| O111_11128 | yijP | EHEC | B1 | 16 | Human |
| Sakai | ECs4884 | EHEC | E | 11 | Human |
| ED1a | yijP | Commensal | B2 | 452 | Human |
| UTI89 | yijP | UPEC | B2 | 95 | Human |
| UPEC_536 | ECP_4168 | UPEC | B2 | 127 | Human |
| CFT073 | yijP | UPEC | B2 | 73 | Human |
| APEC_O1 | yijP | APEC | B2 | 95 | avian |
| EPEC_E2348/69 | yijP | EPEC | B2 | 566 | Human |
| UMN026 | yijP | (ExPEC) | D | 597 | Human |
| IAI39 | yijP | (ExPEC) | D | 62 | Human |
| O7_K1_CE10 | ibeC | NMEC(ExPEC) | D | 62 | Human |
| EAEC_042 | EC042_4330 | EAEC | - | 414 | Human |
| EIEC_53638 | Ec53638_1822 | EIEC | - | 6 | Human |
| O78 | APECO78_00565 | APEC | - | 23 | avian |
| O104:H4_2009EL-2071 | O3M_23975 | EHEC | - | 678 | Human |
| UMNK88 | UMNK88_4793 | ETEC | - | 100 | porcine |
|
| 图 1 25株E.coli代表菌株ibeC基因多序列比对结果 Fig.1 Multi-sequence alignment of ibeC gene identified in 25 representative E. coli strains 注:序列完全一致部分由星号标示,出现碱基差异位点处由点号标示。 |
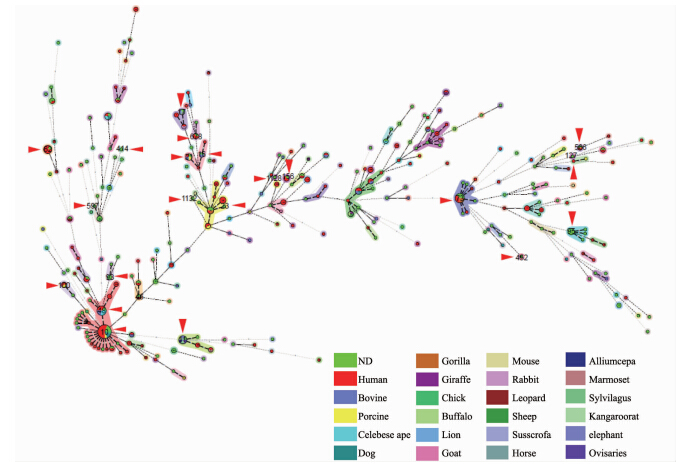
MLST将1620株E.coli分成261个已知ST型,我们选取了其中342株代表菌株,这些菌株包含了261种ST型,根据菌株描述信息,具有23个不同分离来源,分别为人、猪、牛、猿、犬、长颈鹿、鸡、山羊、绵羊、猩猩、老鼠、兔子、雌豹、野猪、野牛、马、美洲狮、洋葱、狨猴、林兔、跳囊鼠、大象、羊胆汁,且具有不同致病表型:EAEC、EPEC、EIEC、ETEC、EHEC、UPEC、NMEC等,通过BioNumerics V 4.0软件,对这些代表菌株及ECOR菌株已知的不同ST型别构建最小生成树,见图 2。由图 2可见,ST10形成优势克隆群,所代表菌株主要为非致病型E.coli,其他致病类型菌株分布在其他不同家系(表 1),与之前研究结果一致[3]。
|
| 图 2 E.coli的ST型最小生成树 Fig.2 Minimum spanning tree of MLST of published E. coli strains 注:每个圆圈中的数据代表一种ST型,不同颜色的圆圈表示菌株不同来源,圆圈大小代表菌株数的多少,圆圈之间的粗细实线分别表示ST 型相差一个或两个等位基因,虚线表示ST 型之间存在3个或以上等位基因差异。圆圈内不同的颜色表示不同E.coli宿主来源。所示菌株为表 1所示E.coli菌株。 |
Ibe是一组NMEC相关大脑内皮细胞侵袭素基因,被明确定义的主要有ibeA、ibeB、ibeC,这些基因对大脑内皮细胞的侵入作用是通过对菌株诱变导致基因缺失,再通过分子生物学实验回补缺失部位而证实的 。研究表明,ibeA、ibeB是具有跨膜结构的外膜蛋白,ibeC具有信号样序列片段和多个跨膜区。NMEC之所以能够侵入HBMEC,是因为Ibe能够和HBMEC胞膜蛋白形成了配体-受体结构,经相互作用后介导NMEC进入HBMEC[7]。在HBMEC胞膜表面发现一个45×103蛋白能够和ibeA相互作用,进一步支持上述结论,对于ibeA基因的毒力相关作用也被进一步证实[8]。关于ibeB的功能研究分析发现ibeB在改变HBMEC细胞骨架及细胞紧密连接特性中发挥作用,证实了NMEC对HBMEC的侵袭有赖于ibeB基因产物对细胞骨架的调节[9]。但是,关于ibeC的毒力功能一直未有明确说法[10]。研究已知ibeC与实验菌株K12 表达脂多糖庚糖I丙醇胺转移酶基因(LPS heptose I phosphoethanolaminetransferase,eptC,yijP)具有高度同源性,ibeC基因功能可能和该基因有关。
本研究发现GenBank现存并公开释放的1620株不同表型、不同来源的E.coli菌株,经ibeC基因检测比对,所有被分析菌株中均存在ibeC基因,且差异微小,说明该基因具有保守性。为了说明菌株的代表性,我们对1620株E.coli进行了MLST分型分析,将其分成261个已知ST型。选取了342株代表菌株,这些菌株包含了261种ST型,同时根据菌株描述信息,具有23个不同分离来源,分别为人、猪、牛、猿、犬、长颈鹿、鸡、山羊、绵羊、猩猩、老鼠、兔子、雌豹、野猪、野牛、马、美洲狮、洋葱、狨猴、林兔、跳囊鼠、大象、羊胆汁,且具有不同致病表型:EAEC、EPEC、EIEC、ETEC、EHEC、UPEC、NMEC等,可以代表目前所有研究分类的大肠埃希菌。为了进一步说明菌株的代表性,我们又加入了MLST数据库中已经明确分群的72株ECOR菌株[4],采用BioNumerics V 4.0软件,对不同来源菌株的不同ST型别构建最小生成树发现(图 2),菌株ST型别与菌株来源无关联性,不同致病型别的菌株分布在不同家系,该菌株结构关系图进一步表明ibeC基因的保守性,这些结果与之前假设结果一致,不同来源、不同致病类型E.coli中ibeC基因高度同源。所以,我们认为ibeC可能并不是NMEC特异的致病相关基因,推测可能是E.coli生存所必需基因,在实验研究中所观察到的致病作用,有可能是因为影响到了E.coli的生长状态而出现的,并非致病性作用,关于该类E.coli致病相关机制还有待研究。本文的发现对于以后研究NMEC的致病机制具有很好的提示作用,也提示此致病机制应该是一种综合作用。
| [1] | Huang SH, Stins MF, Kim KS. Bacterial penetration across the blood-brain barrier during the development of neonatal meningitis[J]. Microbiol Infect,2000,2(10):1237-1244. |
| [2] | Kim KS. Escherichia coli translocation at the blood-brain barrier[J]. Infect Immun,2001,69(9):5217-5222. |
| [3] | Wirth T, Falush D, Lan RT, et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: an evolutionary perspective[J]. Mol Microbiol,2006,60(5):1136-1151. |
| [4] | Wang Y, Huang SH, Wass CA, et al. The gene locus yijP contributes to Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Infect Immun, 1999,67(9):4751-4756. |
| [5] | Huang SH, Chen YH, Fu Q, et al. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli invasion gene locus, ibeB, required for penetration of brain microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Infect Immun,1999,67(5):2103-2109. |
| [6] | Huang SH, Wan ZS, Chen YH, et al. Further characterization of Escherichia coli brain microvascular endothelial cell invasion gene ibeA by deletion, complementation, and protein expression[J]. J Infect Dis,2001,183(7):1071-1078. |
| [7] | Huang SH, Chen YH, Kong G, et al. A novel genetic island of meningitic Escherichia coli K1 containing the ibeA invasion gene (GimA):functional annotation and carbon-source-regulated invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Funct Integr Genomics,2001,1(5):312-322. |
| [8] | Prasadarao NV, Wass CA, Huang SH, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel ibe10 binding protein that contributes to Escherichia coli invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Infect Immun,1999,67(3):1131-1138. |
| [9] | Chen DS. Function analysis of the genes of invasion of HBMEC of E.coli in neonatal meningiti[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University,2005. (in Chinese) 陈冬松. 新生儿脑膜炎大肠杆菌K1株的HBMEC侵袭相关基因功能分析[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学,2005. |
| [10] | Chen LD, Cao H. Advances in mechanism research of meningitis caused by E. coli to penetrate the blood-brain barrier[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses,2005,21(5):426-428. (in Chinese) 陈丽丹,曹虹. 致脑膜炎大肠杆菌穿透血脑屏障机制的研究进展[J]. 中国人兽共患病杂志,2005,21(5):426-428. 扫描微信二维码 关注本刊最新动态 |
 2015, Vol. 30
2015, Vol. 30


