扩展功能
文章信息
- 邵华, 刘炜炜, 么鸿雁, 周脉耕, 刘世炜, 李镒冲, 胡跃华, 于石成
- SHAO Hua, LIU Wei-wei, YAO Hong-yan, ZHOU Mai-geng, LIU Shi-wei, LI Yi-chong, HU Yue-hua, YU Shi-cheng
- 1990-2010年我国新生儿疾病的疾病负担及变化趋势
- Burden of neonatal diseases in China, 1990-2010
- 疾病监测, 2015, 30(8): 663-667
- Disease Surveillance, 2015, 30(8): 663-667
- 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2015.08.014
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2015-04-14
2. 通辽市疾病预防控制中心, 内蒙古 通辽 028000;
3. 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心, 北京 100050
2. Tongliao Prefecture Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Tongliao 028000, Inner Mongolia, China;
3. Chronic & Non-communicable Disease Prevention and Control Center, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 100050, China
新生儿疾病,病因较为复杂,随着医学的进步和新生儿护理的不断发展,其死亡率显著下降,疾病的早期预后已明显得到改善[1],但是,新生儿疾病对相关生命质量引起不同程度的不良影响,导致的发育性残疾增加了疾病负担。与1990年相比,2010年,新生儿疾病年龄标化死亡率中位百分下降了64.5%。但在2010年<5岁年龄组,早产并发症(2)、其他新生儿疾病(3)、新生儿脑病(5)是死因别研究的231种病因百分位数的前5位。新生儿败血症及其他感染性疾病是第16位。早产并发症、新生儿脑病是疾病死亡损失的健康生命年(years of life lost,YLL)研究的第19位和20位。新生儿脑病是疾病伤残损失的健康生命年(years lived with disability,YLD)研究的第27位[2]。可见新生儿疾病仍是我国引起疾病负担的主要疾病。 本报告分性别、年龄组展示我国新生儿疾病的患病数和患病率、死亡数和死亡率,YLL数、YLD数和伤残调整寿命年(disability-adjusted life years,DALY)数以及它们的率。目的是更系统地了解我国不同年龄分组新生儿疾病的疾病负担和20年间变化规律,为合理配置卫生资源和制定卫生政策提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 数据来源2010年全球疾病负担研究(global burden of diseases,injuries,and risk factors study 2010,GBD 2010)收集多个数据来源,包括2004-2005年第3次死因回顾调查、1989-2011年全国疾病监测点系统死因监测、1980-2010年已发表和可利用的未发表的新生儿疾病的文献资料,及全国卫生服务调查、人口调查资料等,在评估数据的完整性、诊断准确性和缺失值后,估算了1990、2000和2010年不 同疾病不同年龄组患病情况、死亡情况及疾病负担指标,使用贝叶斯Meta回归技术,计算了某病不同年龄组YLL率、YLD率和DALY率[2, 3, 4, 5]。笔者从中分性别和年龄组统计分析了新生儿疾病的患病情况、包括以下指标:患病数和患病率,死亡数和死亡率,DALY数和率,YLL数和率,YLD数和率。
1.2 疾病分类与编码把各种疾病利用《疾病和有关健康问题的国际统计分类第十次修订本》(ICD-10)的标准进行编码和归类,对应到GBD 2010病因列表,对不明确的死因诊断重新分配了编码和处理了垃圾编码[6, 7]。本研究报告了4类新生儿疾病:早产并发症、新生儿脑病、败血症和其他感染性疾病及其他新生儿疾病。
1.3 分析方法
以2010年全国人口普查结果为标准人口,分性别报告1990年和2010年<1岁组新生儿疾病的患病数、死亡数和疾病负担指标及它们的标化率,标化率采用直接计算法,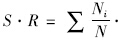
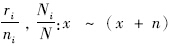 年龄组标准人口构成比,
年龄组标准人口构成比,
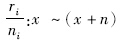 年龄组专率[8],并计算每个指标20年间变化幅度。分疾病类型和0~6、7~27及28~364天年龄组报告患病情况、死亡情况、疾病负担指标及20年间这些指标的增量和增幅。
年龄组专率[8],并计算每个指标20年间变化幅度。分疾病类型和0~6、7~27及28~364天年龄组报告患病情况、死亡情况、疾病负担指标及20年间这些指标的增量和增幅。
患病水平的变化、死亡水平的变化、 DALY的变化、YLL的变化和YLD的变化见表 1。
| 年份 | 患病数(例) | 标化患病率(/1000万) | 死亡数(例) | 标化死亡率(/1000万) | DALY(人年) | 标化DALY率(年/1000万) | YLL(人年) | 标化YLL率(年/1000万) | YLD(人年) | 标化YLD率(年/1000万) |
| 男性 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 127 403.67 | 1.05 | 203 888.32 | 1.67 | 17 583 969.00 | 144.35 | 17 541 149.30 | 143.99 | 42 816.74 | 0.35 |
| 2010 | 75 367.95 | 0.88 | 48 556.00 | 0.56 | 4 200 089.80 | 48.80 | 4 177 299.30 | 48.54 | 22 790.50 | 0.26 |
| 增量 | -52 035.72 | -0.17 | -155 332.32 | -1.11 | -13 383 879.20 | -95.54 | -13 363 850.00 | -95.45 | -20 026.24 | -0.09 |
| 增幅(%) | -40.84 | -16.26 | -76.19 | -66.29 | -76.11 | -66.19 | -76.19 | -66.29 | -46.77 | -24.66 |
| 女性 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 84 899.53 | 0.78 | 138 609.12 | 1.27 | 11 953 591.00 | 109.25 | 11 924 987.00 | 108.98 | 28 604.16 | 0.26 |
| 2010 | 47 381.85 | 0.66 | 34 456.06 | 0.48 | 2 978 491.10 | 41.22 | 2 964 296.00 | 41.02 | 14 195.14 | 0.20 |
| 增量 | -37 517.68 | -0.12 | -104 153.06 | -0.79 | -8 975 099.90 | -68.03 | -8 960 691.00 | -67.96 | -14 409.01 | -0.06 |
| 增幅(%) | -44.19 | -15.49 | -75.14 | -62.36 | -75.08 | -62.27 | -75.14 | -62.36 | -50.37 | -24.86 |
| 合计 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 212 303.20 | 0.92 | 342 497.43 | 1.48 | 29 537 560.00 | 127.74 | 29 466 139.00 | 127.43 | 71 420.90 | 0.31 |
| 2010 | 122 749.80 | 0.78 | 83 012.06 | 0.52 | 7 178 580.90 | 45.34 | 7 141 595.20 | 45.11 | 36 985.65 | 0.23 |
| 增量 | -89 553.40 | -0.14 | -259 485.37 | -0.96 | -22 358 979.10 | -82.40 | -22 324 543.80 | -82.32 | -34 435.25 | -0.08 |
| 增幅(%) | -42.18 | -15.55 | -75.76 | -64.60 | -75.70 | -64.50 | -75.76 | -64.60 | -48.21 | -24.37 |
0~6天组、7~27天组和28~364天组患病情况见表 2。
| 年龄组(d) | 患病数(例) | 患病率(/1000万) | 死亡数(例) | 死亡率(/1000万) | DALY(人年) | DALY率(年/1000万) | YLL(人年) | YLL率(年/1000万) | YLD(人年) | YLD率(年/1000万) |
| 0~6 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 1 296.54 | 2.81 | 83 185.94 | 179.97 | 7 158 297.70 | 15 487.11 | 7 158 090.50 | 15 486.66 | 207.21 | 0.45 |
| 2010 | 893.66 | 2.83 | 22 044.07 | 69.92 | 1 897 017.60 | 6 016.70 | 1 896 876.60 | 6 016.25 | 140.98 | 0.45 |
| 增量 | -402.88 | 0.03 | -61 141.87 | -110.06 | -5 261 280.10 | -9 470.41 | -5 261 213.90 | -9 470.41 | -66.23 | 0.00 |
| 增幅(%) | -31.07 | 1.04 | -73.50 | -61.15 | -73.50 | -61.15 | -73.50 | -61.15 | -31.96 | -0.27 |
| 7~27 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 3 856.75 | 2.80 | 11 024.82 | 8.02 | 948 754.22 | 689.97 | 948 139.72 | 689.52 | 614.51 | 0.45 |
| 2010 | 2 671.86 | 2.83 | 3 789.09 | 4.02 | 326 286.30 | 346.12 | 325 863.45 | 345.67 | 422.85 | 0.45 |
| 增量 | -1 184.89 | 0.03 | -7 235.73 | -4.00 | -622 467.92 | -343.84 | -622 276.27 | -343.85 | -191.65 | 0.00 |
| 增幅(%) | -30.72 | 1.05 | -65.63 | -49.87 | -65.61 | -49.83 | -65.63 | -49.87 | -31.19 | 0.38 |
| 28~364 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 61 940.80 | 2.80 | 3 114.40 | 0.14 | 277 146.66 | 12.55 | 267 455.77 | 12.11 | 9 690.89 | 0.44 |
| 2010 | 42 868.39 | 2.83 | 1 734.08 | 0.11 | 155 582.11 | 10.29 | 148 996.60 | 9.85 | 6 585.51 | 0.44 |
| 增量 | -19 072.40 | 0.03 | -1 380.32 | -0.03 | -121 564.55 | -2.26 | -118 459.17 | -2.26 | -3 105.37 | 0.00 |
| 增幅(%) | -30.79 | 1.08 | -44.32 | -18.65 | -43.86 | -18.01 | -44.29 | -18.63 | -32.04 | -0.75 |
与1990年相比,2010年0~6天组、7~27天组和28~364天组新生儿脑病的患病例数、患病率、死亡例数、死亡率、DALY、DALY率、YLL、YLL率、YLD和YLD率均有明显下降,具体减幅见表 3。
| 年龄组(d) | 患病数(例) | 患病率(/1000万) | 死亡数(例) | 死亡率(/1000万) | DALY(人年) | DALY率(年/1000万) | YLL(人年) | YLL率(年/1000万) | YLD(人年) | YLD率 (年/1000万) |
| 0~6 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 2 763.34 | 5.98 | 96 091.68 | 207.90 | 8 269 288.00 | 17 890.76 | 8 268 620.40 | 17 889.31 | 667.51 | 1.44 |
| 2010 | 1 435.11 | 4.55 | 21 937.48 | 69.58 | 1 888 045.90 | 5 988.25 | 1 887 704.30 | 5 987.16 | 341.65 | 1.08 |
| 增量 | -1 328.23 | -1.43 | -74 154.20 | -138.32 | -6 381 242.10 | -11 902.52 | -6 380 916.10 | -11 902.15 | -325.86 | -0.36 |
| 增幅(%) | -48.07 | -23.87 | -77.17 | -66.53 | -77.17 | -66.53 | -77.17 | -66.53 | -48.82 | -24.97 |
| 7~27天 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 8 219.25 | 5.98 | 10 465.52 | 7.61 | 902 029.12 | 655.99 | 900 039.38 | 654.54 | 1 989.75 | 1.45 |
| 2010 | 4 290.63 | 4.55 | 3 258.14 | 3.46 | 281 230.06 | 298.33 | 280 201.72 | 297.24 | 1 028.34 | 1.09 |
| 增量 | -3 928.63 | -1.43 | -7 207.38 | -4.15 | -620 799.06 | -357.66 | -619 837.66 | -357.30 | -961.40 | -0.36 |
| 增幅(%) | -47.80 | -23.85 | -68.87 | -54.59 | -68.82 | -54.52 | -68.87 | -54.59 | -48.32 | -24.61 |
| 28~364天 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 131 981.91 | 5.97 | 3 032.77 | 0.14 | 291 430.15 | 13.19 | 260 443.68 | 11.79 | 30 986.48 | 1.40 |
| 2010 | 68 844.12 | 4.55 | 1 474.69 | 0.10 | 142 892.45 | 9.45 | 126 709.17 | 8.38 | 16 183.29 | 1.07 |
| 增量 | -63 137.80 | -1.42 | -1 558.08 | -0.04 | -148 537.70 | -3.75 | -133 734.51 | -3.41 | -14 803.19 | -0.33 |
| 增幅(%) | -47.84 | -23.81 | -51.37 | -28.99 | -50.97 | -28.39 | -51.35 | -28.94 | -47.77 | -23.72 |
与1990年相比,2010年新生儿败血症和其他感染性疾病0~6天组患病率增加了14.04%,YLD率增加了14.33%。患病例数、死亡例数、死亡率、DALY、DALY率、YLL、YLL率和YLD均下降。7~27天组和28~364天组死亡例数、死亡率、DALY、DALY率、YLL和YLL率均有明显下降,见表 4。
| 年龄组(d) | 患病数(例) | 患病率(/1000万) | 死亡数(例) | 死亡率(/1000万) | DALY(人年) | DALY率(年/1000万) | YLL(人年) | YLL率(年/1000万) | YLD(人年) | YLD率 (年/1000万) |
| 注:GBD 2010没有给出新生儿败血症和其他感染性疾病7~27天和28~364天年龄组患病数、患病率、YLD及YLD率的数据。 | ||||||||||
| 0~6 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | 2 244.61 | 4.86 | 4 263.81 | 9.22 | 367 362.46 | 794.80 | 366 898.20 | 793.79 | 464.26 | 1.00 |
| 2010 | 1 746.03 | 5.54 | 1 254.91 | 3.98 | 108 346.38 | 343.64 | 107 984.34 | 342.49 | 362.04 | 1.15 |
| 增量 | -498.57 | 0.68 | -3 008.90 | -5.24 | -259 016.08 | -451.16 | -258 913.86 | -451.30 | -102.22 | 0.14 |
| 增幅(%) | -22.21 | 14.04 | -70.57 | -56.85 | -70.51 | -56.76 | -70.57 | -56.85 | -22.02 | 14.33 |
| 7~27 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | - | - | 677.91 | 0.49 | 58 300.75 | 42.40 | 58 300.75 | 42.40 | - | - |
| 2010 | - | - | 278.94 | 0.30 | 23 989.17 | 25.45 | 23 989.17 | 25.45 | - | - |
| 增量 | - | - | -398.97 | -0.20 | -34 311.58 | -16.95 | -34 311.58 | -16.95 | - | - |
| 增幅(%) | - | - | -58.85 | -39.98 | -58.85 | -39.98 | -58.85 | -39.98 | - | - |
| 28~364 | ||||||||||
| 1990 | - | - | 127.27 | 0.01 | 10 929.76 | 0.49 | 10 929.76 | 0.49 | - | - |
| 2010 | - | - | 81.79 | 0.01 | 7 027.61 | 0.46 | 7 027.61 | 0.46 | - | - |
| 增量 | - | - | -45.48 | 0.00 | -3 902.15 | -0.03 | -3 902.15 | -0.03 | - | - |
| 增幅(%) | - | - | -35.74 | -6.08 | -35.70 | -6.08 | -35.70 | -6.08 | - | - |
与1990年相比,2010年0~6天组、7~27天组和28~364天组其他新生儿疾病的死亡例数、死亡率、DALY、DALY率、YLL、YLL率、YLD和YLD率均有明显下降,具体减幅见表 5。
| 年龄组(d) | 死亡数(例) | 死亡率(/1000万) | DALY(人年) | DALY率(年/1000万) | YLL(人年) | YLL率(年/1000万) | YLD(人年) | YLD率(年/1000万) |
| 注:GBD 2010没有给出其他新生儿疾病2010年相应年龄组患病数和患病率的数据。 | ||||||||
| 1990 | 93 996.35 | 203.36 | 8 088 757.60 | 17 500.18 | 8 088 318.90 | 17 499.23 | 438.77 | 0.95 |
| 2010 | 17 588.14 | 55.78 | 1 513 678.40 | 4 800.88 | 1 513 446.60 | 4 800.14 | 231.81 | 0.74 |
| 增量 | -76 408.21 | -147.58 | -6 575 079.20 | -12 699.30 | -6 574 872.30 | -12 699.09 | -206.96 | -0.21 |
| 增幅(%) | -81.29 | -72.57 | -81.29 | -72.57 | -81.29 | -72.57 | -47.17 | -22.55 |
| 7~27 | ||||||||
| 1990 | 23 774.48 | 17.29 | 2 045 916.90 | 1 487.86 | 2 044 616.20 | 1 486.92 | 1 300.73 | 0.95 |
| 2010 | 5 840.75 | 6.20 | 502 933.09 | 533.51 | 502 307.58 | 532.85 | 625.51 | 0.66 |
| 增量 | -17 933.72 | -11.09 | -1 542 983.81 | -954.35 | -1 542 308.62 | -954.07 | -675.22 | -0.28 |
| 增幅(%) | -75.43 | -64.16 | -75.42 | -64.14 | -75.43 | -64.16 | -51.91 | -29.86 |
| 28~364 | ||||||||
| 1990 | 12 742.48 | 0.58 | 1 119 347.10 | 50.67 | 1 094 286.30 | 49.54 | 25 060.80 | 1.13 |
| 2010 | 3 729.97 | 0.25 | 331 551.84 | 21.92 | 320 488.18 | 21.19 | 11 063.66 | 0.73 |
| 增量 | -9 012.51 | -0.33 | -787 795.26 | -28.75 | -773 798.12 | -28.35 | -13 997.14 | -0.40 |
| 增幅(%) | -70.73 | -57.25 | -70.38 | -56.74 | -70.71 | -57.22 | -55.85 | -35.52 |
1990-2010年期间,我国新生儿疾病的死亡情况和疾病负担指标均呈现下降趋势,与YLL相比,YLD下降的幅度比较小,YLL减少了13 363 850.00人年,下降了76.19%,YLD减少了20 026.24人年,下降46.77%。由新生儿疾病导致的发育性残疾增加了疾病负担,提示进一步提高新生儿存活率的同时,也需要重视新生儿疾病的预后,减少由残疾带来的疾病负担。男性的死亡情况和疾病负担指标明显高于女性,2010年死亡数男、女分别为48 556.00例、34 456.06例,标化死亡率分别为0.56/1000万、 0.48/1000万。2010年DALY数男、女分别为4 200 089.80人年、2 978 491.10人年,标化DALY率分别为48.80/1000万、41.22/1000万。
世界卫生组织2012年5月2日发布的《出生太早:早产的全球行动报告》指出,全世界每年有1500万早产儿出生,有100多万早产儿在出生后很快死亡,存活下来的早产儿常忍受着伴随一生的病痛。早产儿存活率不断上升,但其严重的并发症发生率较高[9]。早产并发症的患病率呈现上升趋势,死亡及疾病负担情况总体呈现下降趋势、28~364天年龄组较0~6天,7~28天年龄组下降的幅度小。0~6天年龄组仍是疾病死亡和疾病负担较重的年龄组。0~6天年龄组DALY为1 897 017.60人年,YLL为 1 896 876.60人年,YLD为140.98人年,提示目前造成我国早产并发症的疾病负担主要贡献仍是YLL。为预防早产并发症采取早期干预非常重要。
新生儿脑病,是脑损伤、继发性神经性残疾的潜在因素,是新生儿死亡和残疾的重要原因。2010年新生儿脑病28~364天年龄组是患病数最多的年龄组,28~364天组和0~6天组患病数分别为68 844.12例、1 435.11例。死亡数、死亡率、DALY、DALY率、YLL及YLL率0~6天年龄组是最多的年龄组,28~364天年龄组是YLD最多的年龄组,28~364天年龄组和0~6天年龄组的YLD分别是16 183.29人年、341.65人年。
新生儿败血症往往缺乏典型的临床表现,但病情险恶,进展迅速,抗生素的普遍应用,导致耐药菌株明显增多,常见病原菌均有耐药现象[10]。2010年,新生儿败血症及其他感染性疾病是0~6天年龄组引起YLD率的首位,和1990年相比,有上升趋势,增量为0.14/1000万,增加了14.33%。提示需可靠的检查方法对新生儿败血症尽早的防治。
疾病负担的分析是国家投入和政策有效性强有力的评估方法,本研究分性别、年龄段报告了我国新生儿疾病负担,以期为下一步制定卫生政策、合理配置卫生资源提供依据。
| [1] | Yang P, Li YX. Research progress on the treatment of neonatal encephalopathy[J]. Journal of Medical Research,2013,42(1):193-195. (in Chinese) 杨攀,李元霞.关于新生儿脑病治疗的研究进展[J]. 医学研究杂志,2013,42(1):193-195. |
| [2] | Yang GH,Wang Y,Zeng YX,et al. Rapid health transition in China, 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J]. Lancet,2013,381(9882):1987-2015. |
| [3] | Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs)for 291 diseases and in 21 regions, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J]. Lancet,2012,380(9859):2197-2223. |
| [4] | Wang HD, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Lofgren KT, et al. Age-specific and sex-specific mortality in 187 countries, 1970-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2010[J]. Lancet,2012,380(9859):2071-2094. |
| [5] | Salomon JA, Wang HD, Freeman MK, et al. Healthy life expectancy for 187 countries, 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden Disease Study 2010[J]. Lancet,2012,380(9859):2144-2164. |
| [6] | Lazano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J]. Lancet,2012,380(9859):2095-2128. |
| [7] | Vos T,Flaxman AD,Naghavi M,et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010[J]. Lancet,2012,380(9859):2163-2196. |
| [8] | Mei ST, Xie RY. Calculation method of standardized mortality rate by coefficient[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Statistics,1990,7(2):56-57. (in Chinese) 梅树檀,谢汝英.用系数简化标化死亡率的计算方法[J]. 中国卫生统计,1990,7(2):56-57. |
| [9] | Wang ZL, Yu JL. Burden of diseases of prematurity[J]. Chinese Journal of Perinatal Medicine,2012,15(10):626-630. (in Chinese) 王政力,余加林.早产儿疾病负担[J]. 中华围产医学杂志,2012,15(10):626-630. |
| [10] | Jiang Y. Progress in the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal sepsis[J]. Chinese Journal of Neonatology,2010,25(2):69-72. (in Chinese) 姜毅.新生儿败血症诊疗进展[J]. 中国新生儿科杂志,2010,25(2):69-72. |
 2015, Vol. 30
2015, Vol. 30


