扩展功能
文章信息
- 李路茜, 李振军, 楼永良
- LI Lu-xi, LI Zhen-jun, LOU Yong-liang
- GyrB基因在诺卡菌菌种鉴定中的应用研究
- Identification of Nocardia species based on gyrB Gene
- 疾病监测, 2016, 31(6): 503-506
- Disease Surveillance, 2016, 31(6): 503-506
- 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2016.06.014
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2016-02-04
2. 中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所, 传染病预防控制国家重点实验室, 北京 102206
2. State Key Laboratory for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206, China
诺卡菌(Nocardia,N.),属于诺卡菌种,是一种好氧型机会性致病菌,广泛分布于自然界中,如土壤、灰尘、腐烂的植物、淡水、海水、动物的排泄物等[1]。诺卡菌主要造成免疫功能不全患者的感染,引起肺部、皮肤、脑部以及心血管系统等的损伤[2-5],临床以肺部感染最为常见[6]。近年来,随着免疫抑制患者数量的增加,诺卡菌的感染率也随之逐年上升[7],越来越受到重视。诺卡菌传统的鉴定方法十分繁琐、费时,可能耽误病情造成严重后果。随着分子生物技术的飞速进步,特别是聚合酶链反应技术的发展为快速鉴定诺卡菌提供了可能,本研究采用gyrB基因对诺卡菌菌株鉴定,研究其在临床应用中准确鉴定的可行性。
1 材料与方法 1.1 菌株本研究所用诺卡菌菌株包含14个种共41株(标准菌32株,临床株9株)。标准株均购于德国微生物菌种保藏中心(Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen,DSMZ),临床株为中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所生物安全实验室保存,具体信息见表 1。
| 菌种(英文名) | 总数 | 临床株 | 标准株 | GenBank |
| 脓肿诺卡菌(N. abscessus) | 3 | 1 | 2 | - |
| 非洲诺卡菌(N. africana) | 4 | - | 4 | - |
| 星形诺卡菌(N. asteroides) | 4 | - | 2 | 2 |
| 巴西诺卡菌(N. brasiliensis) | 5 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 短链诺卡菌(N. brevicatena) | 3 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 肉色诺卡菌(N. carnea) | 3 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 盖尔森基兴诺卡菌 (N. cyriacigeorgica) | 7 | 2 | - | 5 |
| 鼻疽诺卡菌(N. farcinica) | 10 | 4 | 6 | - |
| 克鲁吉亚诺卡菌(N. kruczakiae) | 3 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 新星诺卡菌(N. nova) | 5 | - | 4 | 1 |
| 豚鼠诺卡菌(N. otitidiscaviarum) | 6 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 少食诺卡菌(N. paucivorans) | 3 | - | 1 | 2 |
| 南非诺卡菌(N. transvalensis) | 2 | - | 2 | - |
| 老兵诺卡菌(N. veterana) | 4 | - | 2 | 2 |
采用Qiagen试剂盒(德国凯杰)制备细菌DNA,根据试剂盒说明进行操作。
1.3 PCR扩增引物:正向引物:5′-GAG GTC GTC ATG ACC CAG CTG CA-3′,反向引物:5′-GTC TTG GTC TGG CCC TCG AAC TG-3′,经文献查询获得[8]。反应体系: 总体积50 μl,2×Premix TaqTM(TaKaRa)溶液25 μl,引物各2 μl,模板50~100 ng。反应条件: 预变性94 ℃ 5 min;95 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1.5 min,运行30个循环,最后72 ℃延伸10 min。
取5 μl扩增产物,1.5%琼脂糖凝胶160 V电泳30 min,在读胶仪中观察条带位置。扩增产物送至北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司进行产物纯化并使用ABI3730进行测序。
1.4 gyrB基因序列分析及系统发育进化树的建立利用DNAStar/Seqman程序将测得的菌株双向测序序列拼接成单一序列。将拼接好的gyrB序列与GenBank上21株诺卡菌(包括星形诺卡菌2株、巴西诺卡菌2株、少食诺卡菌2株、短链诺卡菌2株等)的gyrB序列用Mega 6.06软件中的Clustal W算法进行多序列比对,参数使用默认值,选择邻接(Neighbor-joining,NJ)法和最大似然(Maximum Likelihood,ML)法分别构建进化树,Bootstrap法生成1000次重复,以结核分枝杆菌(Mycobacterium tuberculosis)824B的gyrB序列作为外群。计算种间及种内相似性使用DNAStar/MegAlign程序完成。
2 结果 2.1 诺卡菌菌种gyrB基因相似性分析gyrB基因序列进行多序列比对和种内及种间相似性度分析,见表 2。14种诺卡菌种gyrB基因种内相似率为94.2%~100%,其中,南非诺卡菌(N. transvalensis)种内相似率最低,为94.2%;老兵诺卡菌(N. veterana)相似率最高,达99.9%~100%。诺卡菌gyrB基因种间相似率约为79.2%~97.6%,非洲诺卡菌(N. africana)和新星诺卡菌(N. nova)两个种之间的相似度最高,为96.7%~97.6%;肉色诺卡菌(N. carnea)和豚鼠诺卡菌(N. otitidiscaviarum)种间相似性最低,为79.2%~79.9%;诺卡菌种间平均相似率为86.9%。
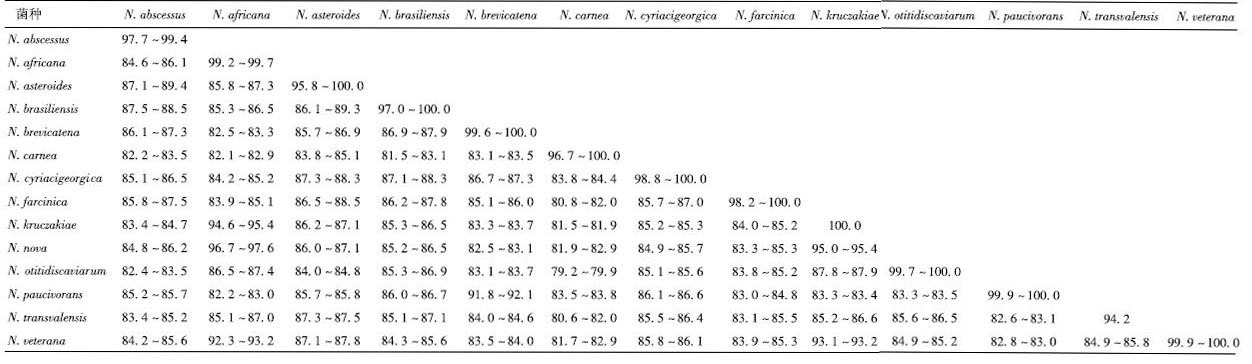
|
采用NJ 和ML法对63株诺卡菌gyrB核苷酸序列构建的进化树,在种属结构上完全一致,图 1只显示以ML法构建的系统发育进化树。可见gyrB基因能很好地将诺卡菌种的各个种属分离开;14种诺卡菌种聚集在不同的14个分支上,同种的诺卡菌种形成一簇,每个分支的支持度均较高(90%)。其中,老兵诺卡菌、新星诺卡菌、非洲诺卡菌、克鲁吉亚诺卡菌之间亲缘关系较近。肉色诺卡菌和新星诺卡菌亲缘关系较远。本研究中不同种的临床株也和相应的诺卡菌种聚集在同一簇。
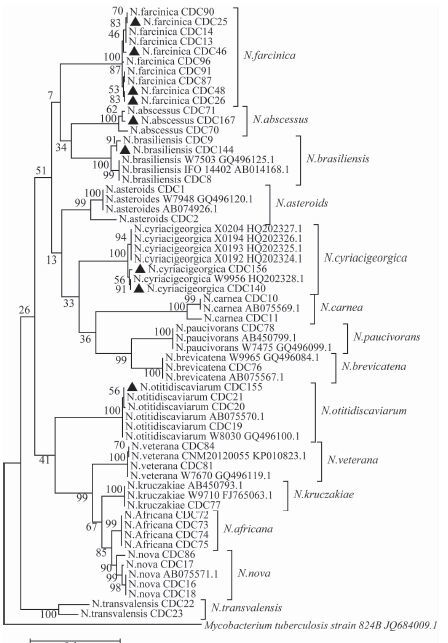
|
| 图 1 本研究诺卡菌和GenBank相关菌株gyrB基因系统发育树 Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree of Nocardia gyrB gene sequences in this study and GenBank |
| |
临床中常见的诺卡菌种感染种类主要有星形诺卡菌、巴西诺卡菌、鼻疽诺卡菌等。由于诺卡菌生长速度十分缓慢,大约1周才能见到菌落,应用传统的生化、药敏鉴定方法鉴定诺卡菌耗时较长、操作繁琐,无法很好地满足临床需要[9]。目前,分子生物学鉴定技术逐渐应用于临床实践。
16S rRNA基因(16S rDNA)是常用的临床鉴定菌株的靶基因[10],已发表的文献对13种诺卡菌菌种进行分型研究,结果显示16S rDNA序列能大致将诺卡菌菌种鉴定至种水平,但由于其保守性较高,种间的相似性在95.7%以上,特别是亚种间的相似性在99.1%~100%,无法将诺卡菌复合体中的亚种进行有效分离[11],因而不能鉴定这些近缘种,限制了其在临床上的广泛应用。促旋酶B单位亚基基因(gyrB)是广泛存在于细菌中的单拷贝管家基因,其进化速率较快,平均碱基替换率为每100万年改变0.7%~0.8%,远远大于16S rRNA基因(进化速率为每5000万年改变1%),而且不发生水平转移[12]。在其他细菌近缘种的鉴定中得到了良好应用,例如沙门菌、芽孢杆菌等[13-14]。故本研究选取gyrB基因作为诺卡菌菌种鉴定的靶基因,并分析其在临床中应用价值。
研究对选取所测的41株诺卡菌序列(32株标准株和9株临床株)和GenBank公布的21株诺卡菌相关序列进行分析,结果表明,诺卡菌种种内相似率均>94%,最高可达100%,说明gyrB基因在诺卡菌种内具有一定保守性。gyrB基因在诺卡菌种种间相似率平均为86.9%,最高相似率不超过97.6%,亲缘关系较近的种间(如老兵诺卡菌,新星诺卡菌、非洲诺卡菌和克鲁吉亚诺卡菌)相似性约为92.3%~97.6%,其余诺卡菌种间相似率为79.4%~89.4%,提示gyrB基因在种间有一定的差异度,在种间甚至于在亲缘关系较近的种间能得到有效区分,因此,在诺卡菌菌种鉴定过程中gyrB基因比16S rDNA具有更好的区分度,能更精准地对诺卡菌菌种做进一步分型。
本研究对14个不同种的62条诺卡菌gyrB序列进行聚类分析,发现gyrB基因能将14种不同的诺卡菌种分为14个不同的群,对于诺卡菌复合体内的亚种(如少食诺卡菌和短链诺卡菌),gyrB基因也能将其分为支持率>90%的不同的独立分支,而16S rDNA无法将这些近缘种进行有效分离。为了验证gyrB基因在临床应用的可靠性,本实验选取了5个不同种临床分离株,在系统发育进化树中这5种临床株能和相应的相同菌种聚集成一簇,进一步验证了gyrB基因在临床应用中的可靠性。
gyrB基因在诺卡菌菌种分型鉴定过程中具有分辨率高的优势,能准确地将诺卡菌鉴定至种水平,为诺卡菌近缘种的鉴定和分析提供了可能。由于诺卡菌种在临床发病率较低,本研究分离得到的临床株有限,若要涵盖更多种类,还需要获取更多菌株以进行更加精准的分型鉴定。其次,gyrB较高的变异性能使PCR引物的通用性下降,进而导致其可操作性降低,16S rDNA的高保守性保障了其广泛使用,因此,gyrB基因在临床应用中可以联合16S rDNA进行鉴定,能更加快速、准确地鉴定诺卡菌菌种。
| [1] | Brown-Elliott BA, Brown JM, Conville PS, et al. Clinical and laboratory features of the Nocardia spp[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2006, 19 (2) : 259–282 . |
| [2] | Bittar F, Stremler N, Audié JP, et al. Nocardia farcinica lung infection in a patient with cystic fibrosis:a case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2010, 4 (1) : 84. |
| [3] | Derancourt C, Theodose R, Deschamps L, et al. Primary cutaneous nocardiosis caused by Nocardia beijingensis[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2012, 167 (1) : 216–218 . |
| [4] | Justiniano M, Glorioso S, Dold S, et al. Nocardia brain abscesses in a male patient with SLE:successful outcome despite delay in diagnosis[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2007, 26 (6) : 1020–1022 . |
| [5] | Naik S, Mateo-Bibeau R, Shinnar M, et al. Successful treatment of Nocardia nova bacteremia and multilobar pneumonia with clarithromycin in a heart transplant patient[J]. Transplant Proc, 2007, 39 (5) : 1720–1722 . |
| [6] | Ambrosioni J, Lew DJ, Garbino J. Nocardiosis:updated clinical review and experience at a tertiary center[J]. Infection, 2010, 38 (2) : 89–97 . |
| [7] | Kageyama A, Yazawa K, Nishimura K, et al. Nocardia anaemiae sp[J]. Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai Zasshi, 2005, 46 (1) : 21–26 . |
| [8] | Carrasco G, Valdezate S, Garrido N, et al. Identification, typing, and phylogenetic relationships of the main clinical Nocardia species in spain according to their gyrB and rpoB genes[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2013, 51 (11) : 3602–3608 . |
| [9] | Wauters G, Avesani V, Charlier J, et al. Distribution of Nocardia species in clinical samples and their routine rapid identification in the laboratory[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2006, 43 (6) : 2624–2628 . |
| [10] | Ward DM, Weller R, Bateson MM. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community[J]. Nature, 1990, 345 (6270) : 63–65 . |
| [11] | Li LX, Zhang YY, Liu HC, et al. Evaluation of 16 S rDNA sequence method in identification of Nocardia species[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2015, 31 (11) : 1017–1022 .(in Chinese) 李路茜, 张媛媛, 刘海灿, 等. 16 S rDNA序列在诺卡菌菌种鉴定中的价值研究[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报,2015,31 (11) :1017–1022. |
| [12] | Li XM, Wang XF, Yang HY, et al. Application of gyrB in the identification of closely related bacteria-a review[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2008, 48 (5) : 701–706 .(in Chinese) 李献梅, 王小芬, 杨洪岩, 等. 促旋酶(gyrase) B亚单位基因gyrB在鉴别细菌近缘种中的应用[J]. 微生物学报,2008,48 (5) :701–706. |
| [13] | Ye XH, Wang YM, Lin XG. A gyrB-targeted PCR for rapid identification of Salmonella[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2011, 63 (5) : 477–483 . |
| [14] | Wang LT, Lee FL, Tai CJ, et al. Comparison of gyrB gene sequences, 16S rRNA gene sequences and DNA-DNA hybridization in the Bacillus subtilis group[J]. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol, 2007, 57 (8) : 1846–1850 . |
 2016, Vol. 31
2016, Vol. 31


