扩展功能
文章信息
- 孙英伟, 毛玲玲, 孙广玖, 刘学升, 雷露, 于维君, 姚文清
- SUN Ying-wei, MAO Ling-ling, SUN Guang-jiu, LIU Xue-sheng, LEI Lu, YU Wei-jun, YAO Wen-qing
- 2012-2015年辽宁省布鲁氏菌病疫情监测结果分析
- Surveillance for brucellosis in Liaoning province, 2012-2015
- 疾病监测, 2017, 32(3): 200-202
- Disease Surveillance, 2017, 32(3): 200-202
- 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2017.03.008
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2016-12-15
布鲁氏菌病 (布病) 是由布鲁氏菌引起的一种人畜共患传染病,是我国法定报告的乙类传染病。辽宁省20世纪60年代开始有系统的病例报告,均为散发病例,发病水平处于较低水平。1989年通过考核验收,达到国家布病控制标准[1]。1994年后局部地区开始有暴发流行,发病数逐渐增多,2004年达到发病高峰后,疫情短暂回落,2007年后又继续缓慢升高[2],是辽宁省重点防制的传染病之一。为了解辽宁省布病流行趋势,现将2012-2015年布病疫情进行分析。
1 材料与方法 1.1 数据来源2012-2015年布病发病资料来自中国疾病预防控制信息系统,病例包括实验室确诊病例和临床诊断病例,按照病例发病时间统计。流行病学、病原学资料由各市按照《全国人间布鲁氏菌病监测方案 (试行)》和《布鲁氏菌病诊断标准》(WS 268 2007)[3]开展监测、调查和实验检测;家畜感染信息参考国家农业部2012-2015年出版的《兽医公报》月刊内蒙古自治区、辽宁省布病疫情报告数据。
1.2 统计学分析收集全省新发病例信息和常规监测数据,用描述性流行病学方法进行对比分析。采用EpiData 3.1软件建立个案数据库,进行数据收集;用Excel 2010和SPSS 19软件对数据进行统计分析。
1.3 实验方法血清学监测,采用试管凝集实验,滴度>1 : 100判定为血清学阳性,试剂由中国疾病预防控制中心 (CDC) 提供;病原学培养为无菌采集患者血液,接种双向血培养瓶,37 ℃培养,可疑菌鉴定参照《布鲁氏菌病防治手册》[4]进行鉴定。
2 结果 2.1 疫情概况2012-2015年辽宁省共报告布病病例9 247例,无死亡病例。其中临床诊断病例153例,实验室确诊病例9 194例。年发病率分别为3.37/10万、4.68/10万、6.37/10万和6.65/10万。4年间,发病数升高1倍,2013年和2014年增幅分别为39.19%和36.24%。
2.2 地区分布14个地级市均有布病病例报告,累计报告病例最多的5个市为葫芦岛市 (2 148例)、锦州市 (1 634例)、阜新市 (1 434例)、沈阳市 (1 206例) 和朝阳市 (935例),5个市共报告布病病例7 357例,占全省报告的79.56%。4年来报告病例的县 (区) 数分别为76、88、97和97个,见图 1。
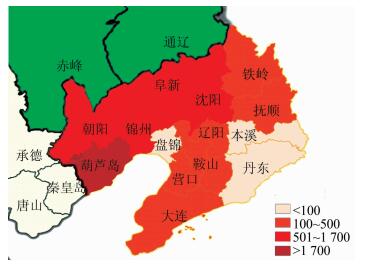
|
| 图 1 2012-2015年辽宁省布病发病地区分布 Figure 1 Area distribution of brucellosis cases in Liaoning, 2012-2015 |
| |
辽宁省布病全年均有发病,有明显的季节性周期,每年只有一个发病高峰 (3-7月),秋冬季发病明显较少。
2.4 人群分布各年龄组均有病例报告,最大为94岁,最小为11月龄。主要集中在36~64岁,占全部病例的78.81%,男女性别比为3.09 : 1。职业分布主要以农民为主,占78.45%,其次是家务待业,占12.46%。
2.5 职业人群监测2012-2015年流行病学调查职业人群63 828人,血清学检测16 656人,阳性1 047人,平均阳性率6.29%。不同年份职业人群血清阳性率比较,差异有统计学意义 (χ2=26.534,P=0.000)。见表 1。
| 年份 | 流调数 | 血检数 | 阳性数 | 阳性率 (%) |
| 2012 | 14 840 | 3 931 | 239 | 6.08 |
| 2013 | 17 527 | 3 873 | 285 | 7.36 |
| 2014 | 16 088 | 3 759 | 268 | 7.13 |
| 2015 | 15 373 | 5 093 | 255 | 5.01 |
| 合计 | 63 828 | 16 656 | 1 047 | 6.29 |
2012-1015年共采集433份疑似患者样品进行病原培养工作,分离到136株布鲁氏菌,其中羊种Ⅰ型32株,占23.52%;羊种Ⅲ型103株,占75.74%;羊种变异型1株。
3 讨论辽宁省2004年以来,报告布病发病的县 (区) 数不断增加,2012年报告发病76个县 (区),2015年增加到97个,占全部县 (区) 数的92.38%(97/105)。全省各地市均有病例报告,主要分布在辽西的葫芦岛、锦州、阜新和朝阳等市。
我国目前引起人发病的布鲁氏菌主要是羊种Ⅲ型[5],辽宁省病原学检测结果与之基本一致[6],结合流行病学调查和实验室监测结果,可以判断目前辽宁省主要的传染源是羊,而羊传播布病的能力远大于牛等其他牲畜[7]。与近几年河北省、内蒙古自治区等检出菌型比较,羊种Ⅰ型较多一些,其原因尚需要进一步研究[8]。
人感染布病主要是接触染病的牲畜所致,布病患者的职业分布显示多数为饲养、放牧和屠宰人员[4]。辽宁省发病人群12.46%为家务、待业人群,这些人与羊的生产繁殖活动并不相关,暴露近年布病已经有转为食源性等非传统传播途径的趋势。事关人民群众民生大事,亟需引起政府足够重视。
从地理位置上看,辽宁省布病发病较多的地市主要是与内蒙古自治区相邻的西部城市,位处交通要道,而内蒙古自治区是布病高流行省份[9-11],近年来畜间疫情不断,每月均有阳性病畜检出,主要为羊和牛。地域上的分布显示,与高发省份的牲畜交易可能是导致该地市布病高发的原因。辽宁省传染源应首先汇集在辽西地区,并逐渐向中部、东部地区扩散,可能是辽宁省布病传染源进入的主要源头,而省内由西至东的牲畜交易流动则为布病疫情的传播路线。病原学监测多位点序列分型显示,内蒙古自治区和辽宁省均为ST8型,提示辽西疫区与内蒙古疫区疫情相关性[12]。之前辽宁省朝阳地区分离到的布鲁氏菌多位点可变数目串联重复序列分析显示出丰富的基因多态性,也侧面证实了这一推测[13]。
减少畜间传染源是控制布病的关键措施,人间疫情的下降依赖于畜间疫情下降[14],但牲畜检疫、免疫和淘汰扑杀存在困难[15]。辽宁省畜间布病疫情与人间疫情的报告有较大差别,多为人间疫情出现暴露畜间疫情情况,进而对畜间疫情进行控制措施,此举对人间疫情控制的效果处于被动局面。
作者贡献:
孙英伟 ORCID:0000-0002-8052-9291
孙英伟:流行病学数据分析
毛玲玲:实验室数据分析
孙广玖:监测数据收集分析
刘学升:实验室检测
雷露:实验室检测
于维君:数据整理
姚文清:监测工作设计管理
| [1] | Sun GJ, Zhao HY, Xu JT. Analysis of the epidemiological characteristics of brucellosis in Liaoning province from 1994 to 2000[J]. Endemic Diseases Bulletin, 2002, 17(2): 36–37. (in Chinese) 孙广玖, 赵恒云, 许景田. 1994-2000年辽宁省布鲁氏菌病流行特征分析[J]. 地方病通报, 2002, 17(2): 36–37. |
| [2] | Sun YW, Mao LL, Li X, et al. Epidemiological analysis of human brucellosis in Liaoning province from 2001 to 2011[J]. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control, 2012, 23(3): 268–269. (in Chinese) 孙英伟, 毛玲玲, 李鑫, 等. 辽宁省2001-2011年布鲁氏菌病流行特征分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2012, 23(3): 268–269. |
| [3] | Ministry of Health of the PRC. WS 268-2007 Diagnostic criteria for brucellosis[S]. Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House, 2007. (in Chinese) 中华人民共和国卫生部. WS 268-2007布鲁氏菌病诊断标准[S]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007. |
| [4] | Xiao DL. Brucellosis prevention manual[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2008: 18-29. (in Chinese) 肖东楼. 布鲁氏菌病防治手册[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 18-29. |
| [5] | Zhou XY, Chen YF, Cui BY, et al. Multiple sequence typing analysis of Brucella melitensis serotype 3 strains[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2011, 27(5): 371–375. (in Chinese) 周晓艳, 陈燕芬, 崔步云, 等. 我国羊种3型布鲁氏菌的多位点序列分型研究[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2011, 27(5): 371–375. |
| [6] | Mao LL, Yao WQ, Geng YZ, et al. The epidemiological situation and typing analysis of brucellosis in Liaoning province from 2004 to 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2010, 26(12): 1170–1172. (in Chinese) 毛玲玲, 姚文清, 耿英芝, 等. 辽宁省2004-2008年布鲁氏菌病流行病学现状及分型分析[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2010, 26(12): 1170–1172. |
| [7] | Wang MW, Gong XS, Shang DQ, et al. The investigation report on brucellosis in Liaoning[J]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 2004, 19(4): 250–254. (in Chinese) 王茂武, 宫新生, 尚德秋, 等. 辽宁省布氏菌病调查报告[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2004, 19(4): 250–254. |
| [8] | Qian ZY, Jiang X, Jia ZY, et al. Analysis on biological characteristics of epidemic Brucella strain in Hebei province[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2013, 40(17): 3266–3268. (in Chinese) 钱振宇, 姜霞, 贾肇一, 等. 河北省布鲁菌流行菌株生物学特征分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2013, 40(17): 3266–3268. |
| [9] | Cui BY, Shang DQ. The situation and analysis of human brucellosis in the national in recent years[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2004, 20(9): 12–14. (in Chinese) 崔步云, 尚德秋. 近年全国人间布鲁氏菌病疫情概况及分析[J]. 中国人兽共患病杂志, 2004, 20(9): 12–14. |
| [10] | Zhao YL, Wang DL, Gang SL, et al. The National surveillance report on brucellosis from 2005 to 2006[J]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 2008, 23(1): 38–40. (in Chinese) 赵永利, 王大力, 冮森林, 等. 2005-2006年布氏菌病全国监测报告[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2008, 23(1): 38–40. |
| [11] | Wang DL, Li TF, Gang SL, et al. Analysis of the monitoring results of brucellosis in the national in 2007[J]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 2008, 23(6): 443–445. (in Chinese) 王大力, 李铁锋, 冮森林, 等. 2007年全国布氏菌病监测结果分析[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2008, 23(6): 443–445. |
| [12] | Xiao P. The epidemiological survey of brucellosis in Inner Mongolia and a comparative study of genotyping methods of Brucella[D]. Beijing:China Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014: 56-57. (in Chinese) 肖培. 内蒙古布鲁氏菌病流行病学调查与布鲁氏菌基因分型方法的比较研究[D]. 北京: 中国疾病预防控制中心, 2014: 56-57. |
| [13] | Mao LL, Jiang H, Lei L, et al. Brucellosis prevalence and MLVA genotyping of Liaoning province in 2010[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2012, 28(12): 1650–1652. (in Chinese) 毛玲玲, 姜海, 雷露, 等. 辽宁省2010年布鲁氏菌病疫情及MLVA分型[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2012, 28(12): 1650–1652. |
| [14] | Liu XL, Sun YQ, Zhao XC, et al. Epidemiological investigation on causes of the decline in the epidemic situation of human brucellosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 2012, 27(1): 40–42. (in Chinese) 刘晓丽, 孙印旗, 赵旭春, 等. 人间布鲁杆菌病疫情下降原因的流行病学调查[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2012, 27(1): 40–42. |
| [15] | Chen D, Liu XL, Liu XG, et al. Epidemic situation and research progress of prevention and control of brucellosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 2011, 26(1): 26–28. (in Chinese) 陈丹, 柳晓琳, 刘孝刚, 等. 布鲁氏菌病流行趋势及其防治措施的研究进展[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2011, 26(1): 26–28. |
 2017, Vol. 32
2017, Vol. 32


