扩展功能
文章信息
- 黄世旺, 徐昌平, 方叶珍, 李剑, 赵雪琴, 李琳
- HUANG Shi-wang, XU Chang-ping, FANG Ye-zhen, LI Jian, ZHAO Xue-qin, LI Lin
- 两种核酸检测法在副溶血性弧菌耐热直接溶血素和不耐热溶血毒素中的应用评估
- Application of two nucleic acid detection methods in evaluation of thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and thermolabilehemolysin (TLH) of Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- 疾病监测, 2016, 31(9): 746-749
- Disease Surveillance, 2016, 31(9): 746-749
- 10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2016.09.009
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2016-06-24
2. 浙江省疾病预防控制中心, 浙江 杭州 310051;
3. 杭州市下城区疾病预防控制中心, 浙江 杭州 310003;
4. 杭州市上城区疾病预防控制中心, 浙江 杭州 310009
2. Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou 310051, Zhejiang, China;
3. Xiacheng District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, Hangzhou 310003, Zhejiang, China;
4. Shangcheng District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, Hangzhou 310009, Zhejiang, China
副溶血性弧菌(Vibrio parahaemolyticus,VP)是沿海地区食物中毒和急性腹泻的主要病原菌[1-2]。误食VP污染食物可导致患者出现腹痛、腹泻、呕吐、发热等症状,若处理不及时,还可引起脱水、昏迷甚至死亡的严重后果。
VP传统检测多以培养法为主,经过增菌、培养、生化鉴定、血清凝集等步骤,操作繁琐、费时费力,不利于VP食物中毒或急性腹泻等的快速诊断。近年来人们陆续采用聚合酶链反应(PCR)、荧光定量PCR等分子生物学技术进行VP诊断[3-4],这对VP的快速检测发挥了重要作用。但PCR、荧光定量PCR均需要昂贵的仪器、技术要求高,不利于在基层或现场推广使用。交叉引物恒温扩增(cross primingamplification,CPA)-核酸试纸条技术是近几年发展起来的一种新的核酸等温扩增检测技术[5],不仅灵敏度高、特异性好,而且不需要昂贵仪器,具有操作简单快捷、容易判定结果等特点,特别适用于基层或现场使用。笔者将该技术引用到VP的快速检测中,陆续建立了检测VP tlh、VP tdh的CPA-核酸试纸条法[6-7],并初步应用于本区2015年4起VP食物中毒临床标本的检测中,获得了较为满意的效果。为了更加客观评价CPA-核酸试纸条法的有效性和实用性,笔者搜集了655株分离自海产品和临床患者的VP菌株,采用CPA-核酸试纸条法和荧光定量PCR 两种方法同时进行了检测比较,现将结果报告如下。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 菌株VP菌株检测的655株海产品和临床分离VP菌株,分别来自杭州市上城区疾病预防控制中心(CDC)(149株)、下城区CDC(159株)和江干区CDC(347株),均为近5年来从外环境海产品监测以及临床腹泻患者(包括医院散发和食物中毒暴发)中分离保存。
对照菌株:共挑选50株非VP的分离菌株作对照,其中5株E.coli、5株P.mirabilis、5株S.aureus、5株S.sonnei、5株B.cereus、3株L.monocytogenes、3株Y.enterocolitica、3株S.typhi、3株S.enteritidis、2株S.flexneri、2株S.dysenteriae由本实验室提供,分别来源于本区历年食物中毒事件和污染物监测项目;2株C.jejuni、2株V.vulnificus、2株E.faecalis、2株P.aeruginosa、1株S.dysenteriae来源于浙江省CDC。
标准菌株:19株标准菌株由浙江省CDC提供。
1.1.2 主要试剂和仪器恒温金属浴采用美国WEALTEC公司的HB-2型,荧光定量PCR仪采用Roche LightCycler 2.0,Bst DNA Polymerase、dNTP与MgSO4均购自英国NEB公司,Betaine购自Sigma公司,封闭式防污染核酸检测装置(内含有核酸检测试纸条)购自杭州优思达生物技术有限公司,Premix Ex TaqTM(Perfect Real Time)购自TaKaRa公司,tlh基因荧光定量PCR检测试剂盒购自深圳生科原生物股份有限公司,tdh基因荧光定量PCR引物、探针序列参考相关文献[4],委托TaKaRa公司合成。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 CPA引物和探针选择根据tlh、tdh保守序列设计CPA引物和探针,包括引物F1和R1,交叉扩增引物CPF和CPR,以及检测探针DRF(5′端标记荧光素FitC)和DRB(5′端标记生物素Biotin)[6-7]。引物和探针委托TaKaRa公司合成。
1.2.2 基因组DNA的制备无菌条件下将655株VP菌株以及13株对照菌株接种于5 ml营养肉汤中,36.5 ℃培养过夜,用基因组DNA提取试剂盒(QIAGEN公司)提取基因组DNA,-80 ℃保存备用。
1.2.3 CPA反应体系的优化CPA以常用20 μl体系为基础,通过改变反应温度,调整引物探针浓度以及调节Bst DNA Polymerase、Betaine、MgSO4剂量进行反应体系的优化,通过分析试纸条的检测结果确定最佳CPA反应体系。
1.2.4 荧光定量PCR反应体系和条件tdh基因荧光定量PCR反应体系和条件参照文献[4],tlh基因荧光定量PCR反应体系和条件参照试剂盒说明书。
1.2.5 病原菌的定量标准以及灵敏度试验无菌操作下接种VP ATCC33847菌株,37 ℃增菌6 h后,平行吸取2份1 ml菌液,1份直接用于基因组DNA的提取;另1份依次作10倍梯度稀释并涂布平板,每个稀释度涂布3块平板进行培养,选取合适稀释度平板计数计算菌液浓度。
对已定量的VP ATCC33847菌液进行10倍梯度稀释,提取基因组DNA,分别用CPA-核酸试纸条法和荧光定量PCR法进行tlh、tdh检测,比较二种方法敏感性。
1.2.6 特异性试验选取10株临床分离VP菌株、10株海产品分离VP菌株与19株标准菌株(VP ATCC 33847、VP ATCC 17802和17株非VP的标准菌株)及50株非VP的分离菌株提取DNA,同时采用CPA-核酸试纸条法和荧光定量PCR法进行tlh、tdh检测,验证方法的特异性。
2 结果 2.1 CPA最佳反应体系的确立经过优化后的tlh、tdh CPA最佳反应体系,包含:Buffer(1×)、dNTP(0.4 mmol/L)、Betaine(0.5 mol/L)、MgSO4 (3 mmol/L)、F1(0.2 μmol/L)、R1(0.2 μmol/L)、CPF(0.8 μmol/L)、CPR(0.8 μmol/L)、DRF(0.4 μmol/L)、DRB(0.6 μmol/L)、Bst DNA Polymerase(0.4 U/ μl)、模板DNA 2 μl,补ddH2O至总体积20 μl;CPA反应条件为63 ℃恒温扩增35 min。
2.2 两种方法检测VP菌株tlh与tdh的敏感性对已定量的VP ATCC 33847菌液(原始浓度为6.2×108 cfu/ml)进行10倍梯度稀释至6.2×100 cfu/ml,各取200 μl提取DNA,分别进行tlh、tdh的CPA-核酸试纸条法与荧光定量PCR法检测,结果表明:两种方法对tlh、tdh的检出限均为6.2×103 cfu/ml。CPA-核酸试纸条法与荧光定量PCR法的检测灵敏度相当。
2.3 两种方法检测VP菌株tlh与tdh的特异性对10株临床分离VP菌株、10株海产品分离VP菌株、VP ATCC 33847、VP ATCC 17802、E.coli ATCC 25922、Y.enterocolitica ATCC 23715、S.paratyphi 50001、S.enteritidis 50335、S.typhimurium ATCC 14028、S.typhi 50013、S.flexneri 51573、S.sonnei 51334、S.dysenteriae 51105、L.monocytogenes ATCC 54003、C.jejuni
ATCC 33291、V.vulnificus ATCC 27562、E.faecalis ATCC 29212、P.aeruginosa ATCC 15442、P.mirabilis ATCC 12453、B.cereus ATCC 63301、S.aureus ATCC 25923和50株非VP的分离菌株分别提取核酸,同时采用CPA-核酸试纸条法和荧光定量PCR检测tlh、tdh,除10株临床分离VP菌株和VP ATCC 33847显示tlh、tdh均阳性,10株海产品分离VP菌株和VP ATCC 17802显示tlh阳性外,其余非VP的标准株和分离株tlh、tdh以及10株海产品分离VP菌株、VP ATCC 17802的tdh检测结果均为阴性,说明CPA-核酸试纸条法与荧光定量PCR法均对VP tlh、tdh具有良好的特异性。
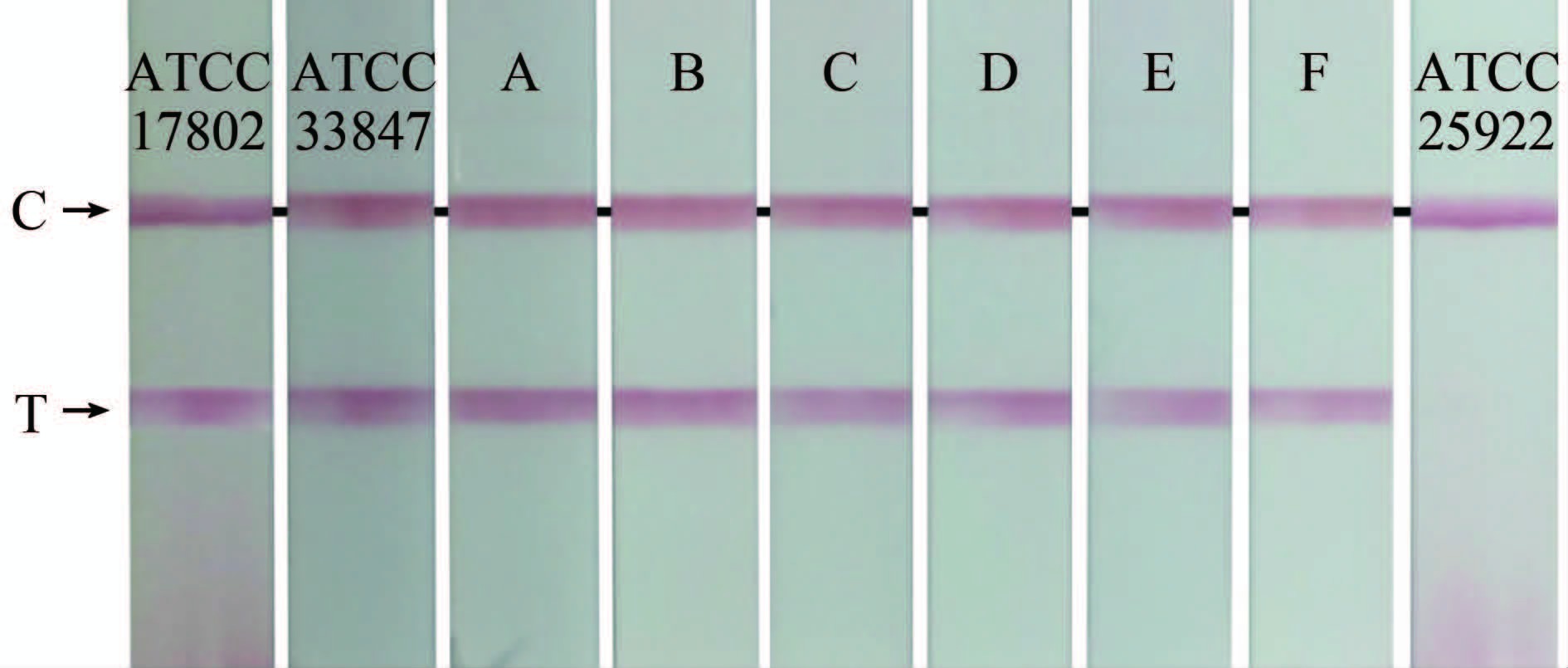
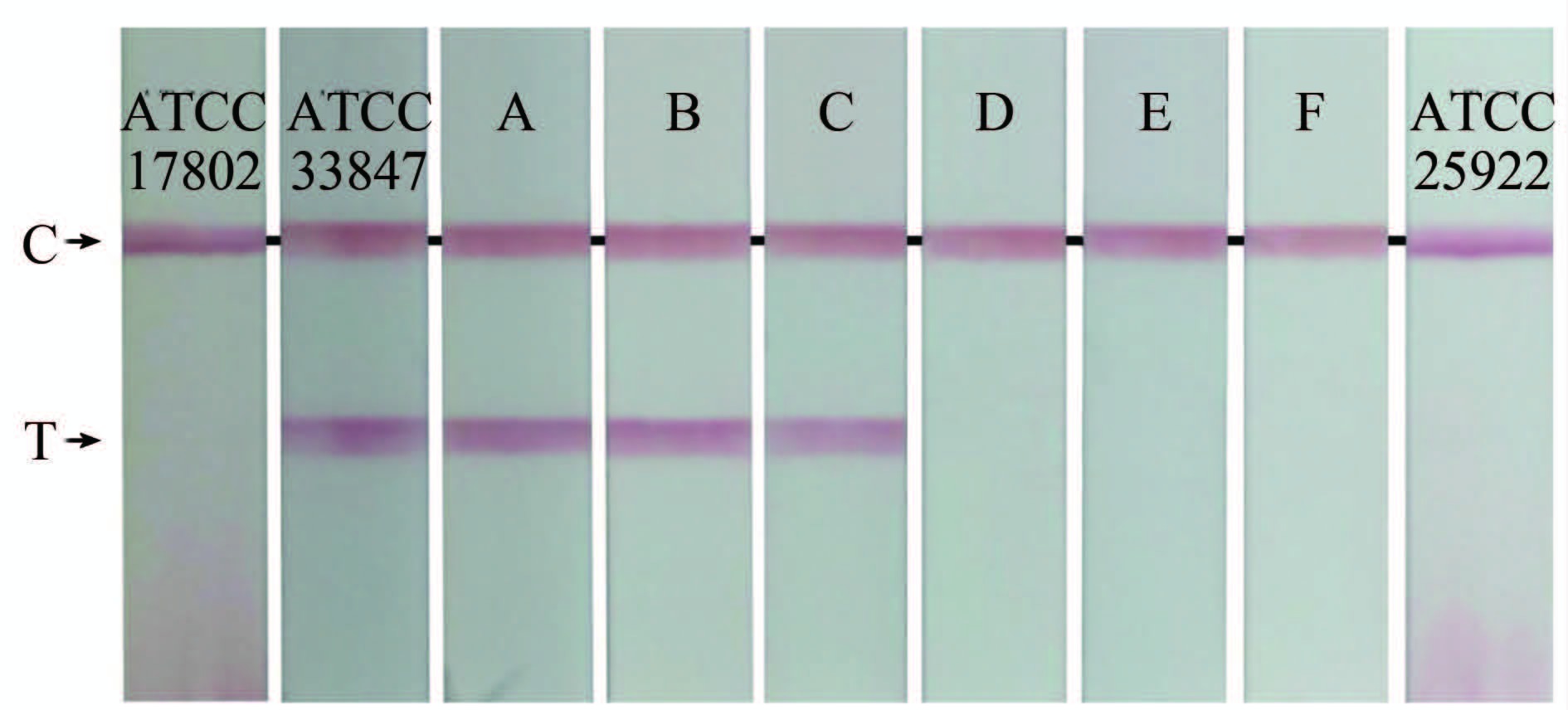
2.4 CPA-核酸试纸条法和荧光定量PCR法检测结果比较利用CPA-核酸试纸条法和荧光定量PCR法同时对655株不同来源VP菌株进行tlh、tdh检测,结果完全一致,显示所有VP菌株均含有tlh种特异性基因;临床分离VP菌株tdh毒力基因阳性率高达95.8%(207/216),海产品分离VP菌株tdh毒力基因阳性率仅2.28%(10/439)。见表 1,图 1、2。
| 菌株来源 | 菌株数量 | tdh阳性数 | tlh阳性数 | ||
| CPA法 | 荧光定量PCR法 | CPA法 | 荧光定量PCR法 | ||
| VP临床分离株 | |||||
| 上城区CDC | 51 | 49 | 49 | 51 | 51 |
| 下城区CDC | 53 | 51 | 51 | 53 | 53 |
| 江干区CDC | 112 | 107 | 107 | 112 | 112 |
| 小计 | 216 | 207 | 207 | 216 | 216 |
| VP海产品分离株 | |||||
| 上城区CDC | 98 | 2 | 2 | 98 | 98 |
| 下城区CDC | 106 | 3 | 3 | 106 | 106 |
| 江干区CDC | 235 | 5 | 5 | 235 | 235 |
| 小计 | 439 | 10 | 10 | 439 | 439 |
|
| 图 1 CPA-核酸试纸条法检测不同来源VP菌株tlh Figure 1 Detection of tlh of V. parahaemolyticus strains from different sources with CPA -nucleic acid test strip |
| |
|
| 图 2 CPA-核酸试纸条法检测不同来源VP菌株tdh Figure 2 Detection of tdh of V. parahaemolyticus strains from different sources with CPA -nucleic acid test strip |
| |
VP的主要致病机制是由于VP可产生多种溶血毒素,包括耐热直接溶血素(thermostable direct hemolysin,TDH)、耐热直接相关溶血素(TDH-related hemolysin,TRH)和不耐热直接溶血素(thermolabile hemolysin,TLH),分别由tdh、trh、tlh编码,其中tlh具有种特异性,tdh、trh与VP致病能力密切相关[8],但研究发现trh无论在海产品还是临床分离VP菌株中均极少检出,而tdh常存在于VP临床分离株中[9-10]。因此,选择tlh、tdh进行研究,对鉴别VP菌株以及VP菌株是否携带毒力基因具有更好的代表性。
在分别建立tlh、tdh CPA-核酸试纸条法的基础上,将其与荧光定量PCR法进行了灵敏度、特异性方面的比较;并同时采用两种方法对655株不同来源VP菌株进行了tlh、tdh检测。结果表明,CPA-核酸试纸条法与荧光定量PCR法检测灵敏度相当,均可达6.2×103 cfu/ml菌液,特异性良好,与17种其他细菌标准株和分离株均不发生交叉反应,对655株VP菌株检测结果完全相同,此外CPA-核酸试纸条法不需使用专业昂贵的荧光定量PCR仪,操作更加简单,可考虑应用于基层实验室以及食源性疾病事件的现场快速检测。
研究结果显示,655株VP菌株均携带tlh种特异性基因,阳性率100%;而tdh毒力基因临床株阳性率95.8%(207/216),海产品株阳性率2.28%(10/439),二者差异有统计学意义,说明海产品VP株仅极少数携带tdh毒力基因,而临床VP株绝大多数均含有tdh毒力基因,提示相关部门加大VP临床患者的搜索力度减少外环境海产品VP的重复监测。
| [1] | Liu XM, Chen Y, Guo YC, et al. Foodborne diseases outbreaks in 2005-report of national foodborne diseases surveillance network in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene , 2008, 20 (6) : 506–509. (in Chinese) 刘秀梅, 陈艳, 郭云昌, 等. 2005年中国食源性疾病暴发事件监测资料分析[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志 , 2008, 20 (6) : 506–509. |
| [2] | Chen J, Zhang RH, Zhang HX, et al. Epidemiological analysis of foodborne disease incidents in Zhejiang province from 2010 to 2012[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene , 2015, 27 (2) : 120–123. (in Chinese) 陈江, 章荣华, 张荷香, 等. 2010-2012年浙江省食源性疾病事件流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志 , 2015, 27 (2) : 120–123. |
| [3] | Zhang HH, Fan JZ, Zhang WY, et al. Detection of virulence factors of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by real-time PCR[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology , 2006, 16 (11) : 1313–1315. (in Chinese) 张红河, 范建中, 张卫英, 等. 实时荧光聚合酶链反应检测副溶血弧菌致病基因[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志 , 2006, 16 (11) : 1313–1315. |
| [4] | Zhang W, Pan JC, Meng DM, et al. Development of multiplex real-time PCR for detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae and Virbio parahaemolyticus[J]. MicrobiologyChina , 2007, 34 (5) : 950–954. (in Chinese) 张蔚, 潘劲草, 孟冬梅, 等. 多重实时PCR检测产毒素性霍乱弧菌和副溶血弧菌[J]. 微生物学通报 , 2007, 34 (5) : 950–954. |
| [5] | Xu GL, Hu L, Zhong HY, et al. Cross priming amplification: mechanism and optimization for isothermal DNA amplification[J]. Sci Rep , 2012, 2 : 246. |
| [6] | Xu PH, Zhou XH, Sun MH, et al. Application of the isothermal amplification method combined with nucleic acid test strip for detection of Vibrio parahemolyticus[J]. International Journal of Epidemiology and Infectious Disease , 2015, 42 (1) : 55–57. (in Chinese) 徐佩华, 周晓红, 孙明华, 等. 恒温扩增-核酸试纸在副溶血性弧菌快速检测中的应用[J]. 国际流行病学传染病学杂志 , 2015, 42 (1) : 55–57. |
| [7] | Huang SW, Lu YY, Li J, et al. Rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin gene by cross primer amplification technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology , 2016, 26 (13) : 1906–1908. (in Chinese) 黄世旺, 卢亦愚, 李剑, 等. 交叉引物恒温扩增技术快速检测副溶血性弧菌耐热直接溶血素基因[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志 , 2016, 26 (13) : 1906–1908. |
| [8] | DePaola A, Ulaszek J, Kaysner CA, et al. Molecular, serological, and virulence characteristics of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from environmental, food, and clinical sources in North America and Asia[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol , 2003, 69 (7) : 3999–4005. DOI:10.1128/AEM.69.7.3999-4005.2003 |
| [9] | Jin ZH, Song DF, Gu Q. The detection of virulence genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology , 2008, 8 (3) : 143–146. (in Chinese) 金周浩, 宋达锋, 顾青. 副溶血弧菌毒力基因的检测研究[J]. 中国食品学报 , 2008, 8 (3) : 143–146. |
| [10] | Fang YZ, Huang SW, Bao FZ, et al. Research on distribution, serogroups and virulence genes of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in different samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology , 2013, 23 (16) : 3222–3224. (in Chinese) 方叶珍, 黄世旺, 包芳珍, 等. 不同来源样品副溶血性弧菌分布现状及血清学和毒力基因研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志 , 2013, 23 (16) : 3222–3224. |
 2016, Vol. 31
2016, Vol. 31


